Highlights
- AWS launches Fastnet, a 320+ Tbps subsea fiber optic system connecting Maryland (U.S.) and County Cork (Ireland) to boost global cloud connectivity.
- Built for AI and edge computing, Fastnet supports high-capacity, low-latency data flows critical for generative AI, ML, and real-time workloads.
- Enhanced network resilience with route diversity, optical-switching branching units, and near-shore protection for long-term reliability.
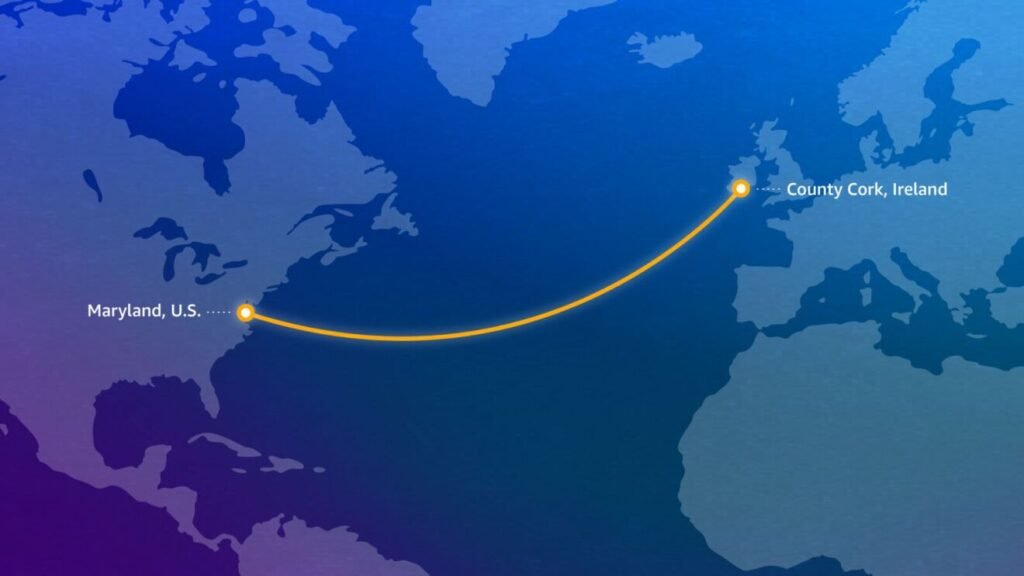
AWS is announcing Fastnet, a high-capacity subsea fiber optic cable system dedicated to the U.S. and Ireland. This infrastructure development will add a new strategic data route between Maryland and County Cork to meet the increasing need to leverage cloud computing, generative AI, edge infrastructure, and global businesses.
What is Fastnet & why it matters
The system is intended to land in Maryland (U.S.) and County Cork (Ireland).
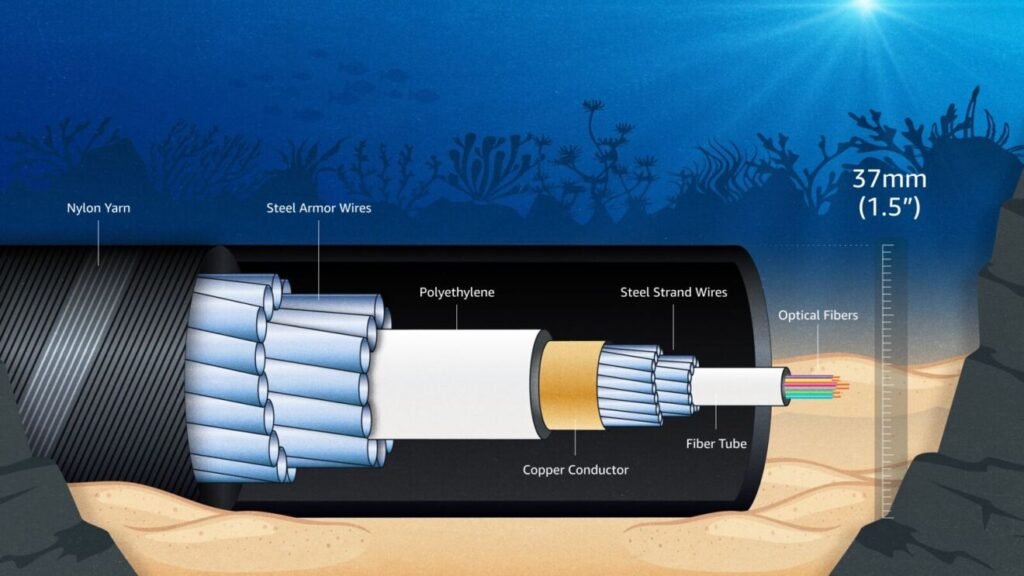
- Designed capacity: 320+ terabits per second (Tbps) — described by AWS as “enough to stream 12.5 million HD films simultaneously”.
- Purpose: Provide alternative route diversity away from congested/traditional cable corridors, enhancing resilience and scalability for AWS’s global network.
- Technology highlights: Incorporates advanced optical-switching branching units to enable future landing points and topology flexibility, and enhanced near-shore protection (steel armoring) to mitigate natural/human risks.
Strategic considerations for AI and Cloud infrastructure
As demand for AI and cloud computing continues to grow (mainly due to edge and global-scale workloads), backbone connectivity, such as Fastnet, will be a key enabler.
For AWS customers, this translates to higher-quality connectivity with lower latency across the Atlantic and greater assurance against service outages or latency, which is especially critical for latency-sensitive applications, live data replication, global enterprises, and AI/ML pipelines.
The landing in Ireland solidifies Europe as a primary cloud gateway, and for the U.S. East Coast (Maryland) it solidifies AWS’s position as the data hub and connectivity node. From a competitive standpoint, investments like this give AWS further “own infrastructure” leverage, rather than relying solely on third-party carrier paths.
Key takeaways
- Transatlantic subsea cable: Fastnet is a TRANSCONTINENTAL subsea fibre-optic system linking the U.S. and Europe, enabling alternative paths for data movement.
- Cloud connectivity infrastructure: This investment highlights AWS’s focus on cloud connectivity, with high-capacity backbone and expanded global network infrastructure.
- AI & edge computing ready: The Fastnet system is built to support generative AI, edge apps, and real-time workflows, with greater capacity (320 Tbps+) and flexible branching units built into the design.
- Network resilience & route diversity: The new landing points and cable route provide redundancy in the event.
- Global data centre connection: By strengthening the cloud infrastructure linking the US with Ireland, AWS further improves trans-Atlantic availability and data flow within its data centre network.
Local community impact and engagement
AWS is making it clear that this is not simply an infrastructure investment: the company will create Community Benefit Funds for both Maryland’s Eastern Shore and the local community in County Cork that can broadly support local initiatives including STEM education, workforce development, sustainability and inclusion programs.
What this means for stakeholders
Fastnet is announced today, 4 November 2025. The cable system is expected to be operational by about 2028. In the next few years, AWS will connect Fastnet to its global network, which spans many geographies, availability zones and millions of kilometers of fiber.
- Enterprises and cloud customers: More reliable transatlantic connectivity, specifically for Europe-US workloads, backups, AI training and multi-region replication.
- AI workload operators: The scale capacity and branching flexibility means growing AI traffic flows can be managed more efficiently.
- Telecom & subsea infrastructure sector: Signals a growing vertical integration by major cloud providers into physical-layer connectivity.
- Global internet resilience: Provides redundancy to the worldwide internet backbone, which is increasingly important given escalating risks (natural disasters, etc.).
Regional economic implications (Ireland & Maryland) – potential jobs created, local infrastructure upgrade, and elevated status as a digital hub.

Final comments
With Fastnet, AWS is building the next generation of cloud-based, AI-ready global infrastructure, not just putting more fibre in the ocean. As data flows increase, latency-sensitive workloads grow, and demands for edge/AI grow, owning and optimising the physical layer is a strategic necessity.
For businesses, it means an infrastructure bet on resiliency, capacity, and connectivity into the future. For regions like Ireland and Maryland, it means enhanced status as unique nodes and hubs in the broader global digital economy.
In summary, AWS is not just playing the cloud game here – it is rewiring the ocean floor for what the next decade will look like.
